It is important to follow real-time air quality updates – particularly children, the elderly, and people suffering from heart and lung disease can be protected. They are at greater risk from fine particulate matter, the primary pollutant in wildfire smoke.
The Getty Fire
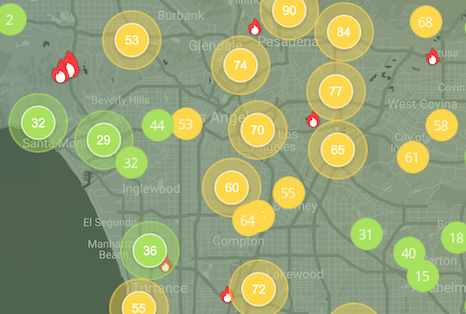
Getty Fire air pollution map
Even early in its development, the Getty fire in Los Angeles spanned more than 600 acres, from Topanga to Bel Air.
The Getty fire, which is believed to have started on Sunday at 11:30pm (local time), quickly grew overnight to 600 acres in just 12 hours. The affected area included affluent Los Angeles neighborhoods of Brentwood and Bel Air – among the 10,000 homes promptly evacuated Monday morning are the homes of NBA basketball player Lebron James and actor Arnold Schwarzenegger.
A crew of more than 1,100 firefighters helped to extinguish much of the fire, though some areas continued to smolder for quite some time, and only 5% of the fire was contained for a long period of time.1
Details as to how the fire started remain unknown. At a news conference on Monday October 28 2019, Los Angeles Mayor Eric Garcetti announced that an arson investigation.2
The Kincade fire
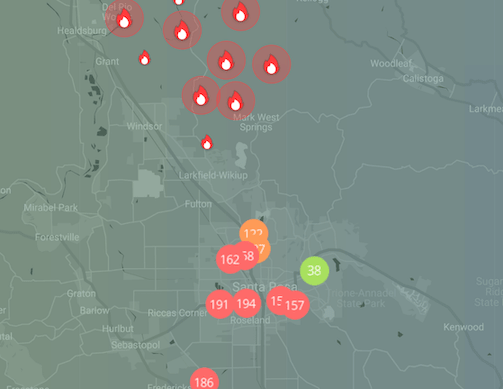
Kincade fire air pollution map
The Kincade fire burning in Sonoma County doubled in size in a matter of hourst and pushed quickly south towards Santa Rosa.
The Kincade fire, which burned through Northern California’s famous winemaking region known as Sonoma County, was the largest active fire in California during this spate of fires. At one point, it was more than 100 times the size of Los Angeles’s Getty Fire.
From the time the fire ignited on October 23 to the following day, it devastated more than 66,000 acres and forced the evacuation of 185,000 local residents.3
While the origin of the fire remains under investigation, a broken jumper cable discovered near a Pacific Gas and Electric Company (PG&E) transmission tower points to faulty equipment as a possible cause.4 A jumper cable carries electrical current that can spark and ignite nearby dry brush.
Strong winds caused the Kincade fire to grow significantly in size and quickly brought the threat to Santa Rosa, where the majority of the area’s population resides.
Bay Area fires (Vallejo, Crockett, and Grizzly Island Fires)
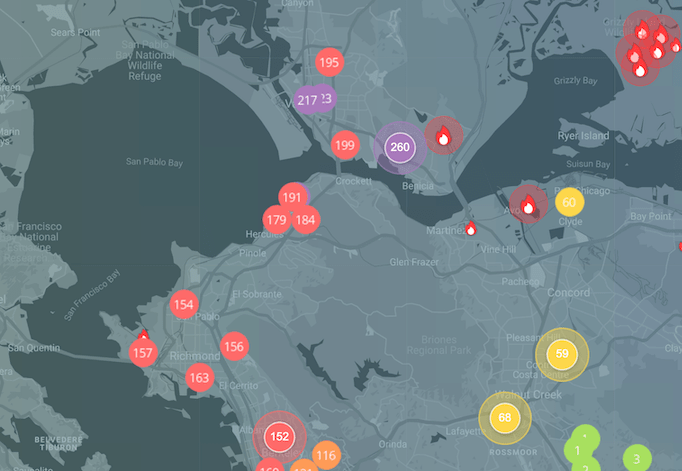
Bay Area fires air pollution map
The Vallejo, Crockett, and Grizzly Island Fires burning on all sides of Grizzly Bay also contributed to unhealthy pollution across the Bay Area.
A vegetation fire on Grizzly Island burned through 2,000 acres in a matter of hours. Firefighters said at the time that they expected it to continue burning for a number of days, but it quickly stopped spreading.
The smoke, however, spread to the San Francisco Bay area, where high-profile organizations like Facebook, Google, and Stanford University are based. The Air Quality Index hit 198 in Palo Alto and 176 in Mountain View shortly after the blazes first ignited. At these unhealthy levels of air quality, everyone began to experience some adverse health effects.
At one point, the AQI in Menlo Park reached 214, according to the IQAir AirVisual air quality map, which reports from more than 2,500 government and nongovernment ground-based stations in California.
The number one air cleaning solution for your home.
Lorem ipsum Donec ipsum consectetur metus a conubia velit lacinia viverra consectetur vehicula Donec tincidunt lorem.
TALK TO AN EXPERTArticle Resources
Article Resources





